AI for Biodiversity
The Challenge
Invasive Aquatic Species (IAS), by growing in an ecosystem not adapted to the presence of a new species, significantly alter population dynamics, causing biodiversity loss and reducing the quality of life for local communities. For example, they clog waterways, hinder recreational and tourism activities, and may even pose risks to human health. At the same time, the traditional management of IAS entails high costs for public administrations and relevant authorities, often proving unsustainable in the long term.
The European Union periodically publishes a list of invasive alien species that threaten biodiversity, habitat integrity, and human activities, with significant economic repercussions. This issue is also evident in the Turin area, which is the focus of the project, particularly in two pilot zones of the Po River: one near the Murazzi area and the other in Villafranca. In both locations, the proliferation of invasive species has become problematic due to various factors, including climate change, negatively impacting native species, tourism, and the local population, causing numerous challenges.
The Project: Innovation Serving Sustainability
This project aims to analyze and propose strategic tools for the reuse of resources, transforming them from an environmental issue into a sustainable opportunity within a Circular Economy framework, generating new economic flows and reducing environmental impact. The project leverages “AI for Biodiversity”—from monitoring IAS to mapping river ecosystems and optimizing management strategies—with a highly interdisciplinary team that ensures a holistic vision and promotes cutting-edge sustainable solutions.
Zirak and Studio Fieschi, SMEs specializing in Green ICT and Footprint/Circular Economy, in collaboration with a leading Research Organization (UNITO – Ecology of Waters and Biochemistry), will develop three functional components, to be tested in a pilot project promoting biomass utilization for energy, pharmaceutical, cosmetic, and nutraceutical purposes:
- The first component, LAB, focuses on laboratory research exploring the potential of biomass, with particular attention to green energy production and the extraction of high-value biomolecules for pharmaceutical, cosmetic, and nutraceutical applications.
- The second component, AI, represents the technological innovation required to track species using aerial data, quantify resource abundance through the creation of bespoke datasets, artificial intelligence models, and map its distribution.
- The third component, LCA, focuses on Life Cycle Analysis, aiming to assess the potential impact of different utilization options in terms of circular economy and environmental sustainability.
These three components work synergistically to create a flexible and modular platform, applying AI techniques to aerial data for precise biomass monitoring and mapping, generating tangible benefits across various domains:
- Economic: Transforming waste into resources, creating jobs, and adding value to local resources.
- Environmental: Reducing waste, protecting biodiversity, and conserving habitats while decreasing the need to extract non-renewable natural resources.
- Social: Mitigating human health risks associated with invasive species and promoting a balanced ecosystem.
- Political: Strengthening territorial resilience and strategically positioning the Piedmont region in sustainable technologies.
The project aligns with a broader corporate strategic initiative focusing on various challenges of the river ecosystem. Currently in the prototyping phase, it enables the analysis of abnormal conditions within a river or its surrounding area.
RiparianEye – features

Zirak’s Role
As project lead, Zirak conceived the RiparianEye – Biomass project and is developing the End-to-End platform, which includes:
- Pre-processing of aerial data (satellite and multispectral images)
- Management of large datasets via a custom-designed backend
- Integration of field data provided by project partners
- Development and fine-tuning of the necessary Computer Vision and Artificial Intelligence algorithms
- Analysis of various vegetation indices, multispectral bands, and their combinations
- Early alert management
- Presentation layer through an effective and intuitive frontend
Zirak’s objective, by channeling its expertise through RiparianEye, is to become a key player in the circular economy in Piedmont, leveraging tools such as Big Data Analytics, Computer Vision, and Artificial Intelligence.
An Intelligent and Intuitive Interface
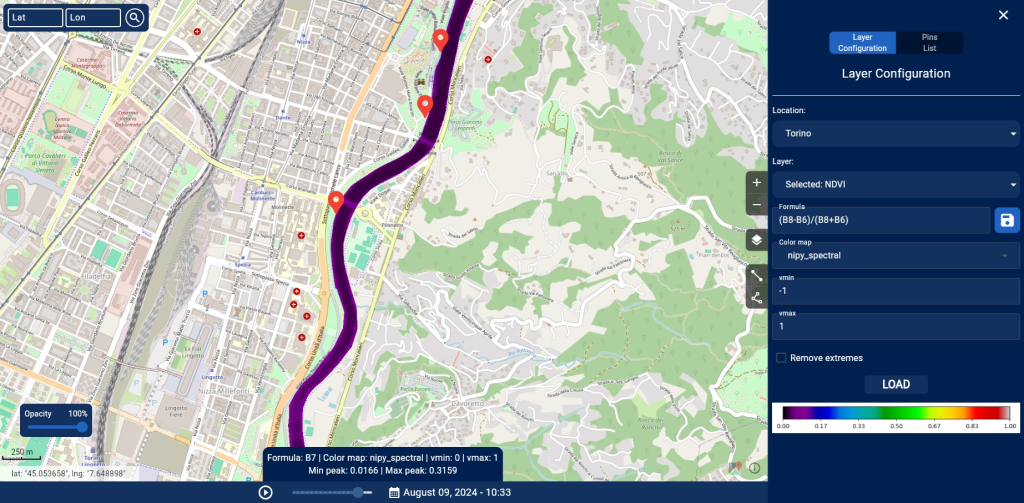
Our frontend combines interactive geospatial visualizations, advanced analytical tools, and personalized data management to transform complex information into actionable decisions. With a modular and responsive design, it ensures seamless performance on any device and offers:
- Dynamic maps to explore raster and vector data with customizable filters.
- Analytical tools such as temporal analysis, custom formulas, and intelligent notifications.
- Personalized dashboards to manage data, preferences, and reports effortlessly.
The frontend is designed to be scalable, extensible, and fully interoperable with geospatial standards.
It provides an interactive geospatial platform for analyzing environmental and territorial data, enabling:
- Visualization of raster and NDVI data, highlighting areas with varying vegetation intensity using a color scale (e.g., from red to green).
- Configuration tools for indices and desired bands, defining custom formulas, adjusting minimum/maximum values, and selecting color maps.
- Complete map interaction, allowing users to navigate, adjust layer opacity, and add annotations or custom pins.
- Temporal analysis, enabling comparative analysis of data over time.
- Custom output generation.
- Dynamic interaction with tools to navigate the map, adjust layer opacity, and add annotations or custom pins.
This interface is designed to support decisions based on environmental data, facilitating vegetation monitoring, land-use planning, and natural resource analysis.
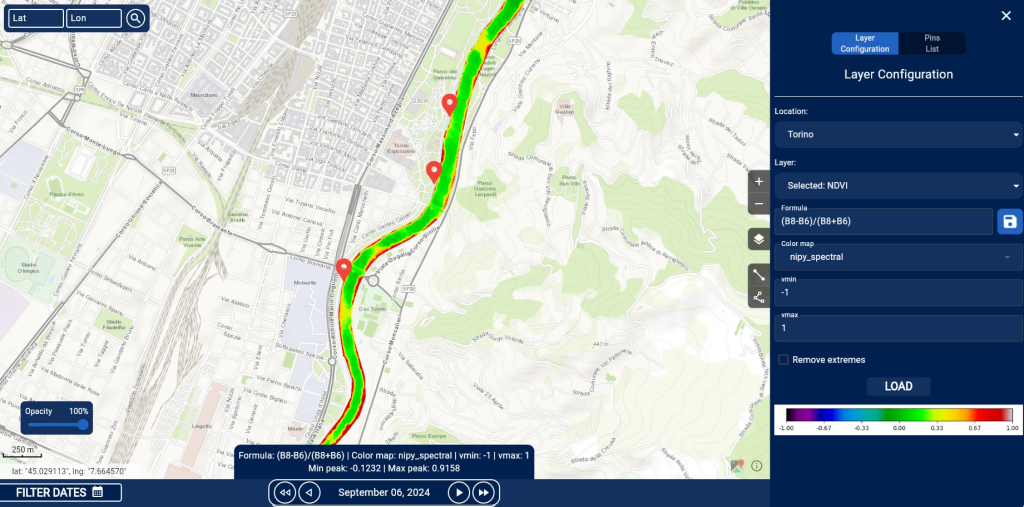
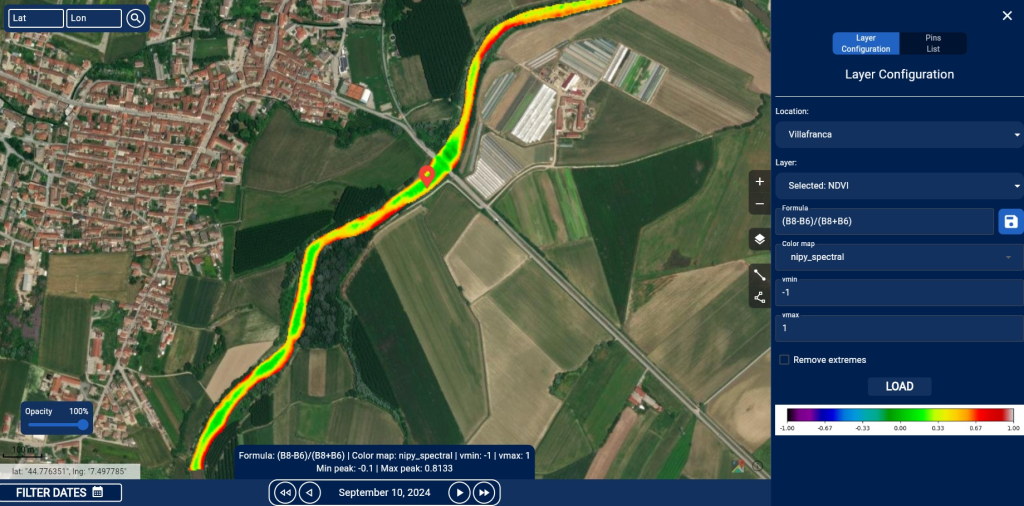
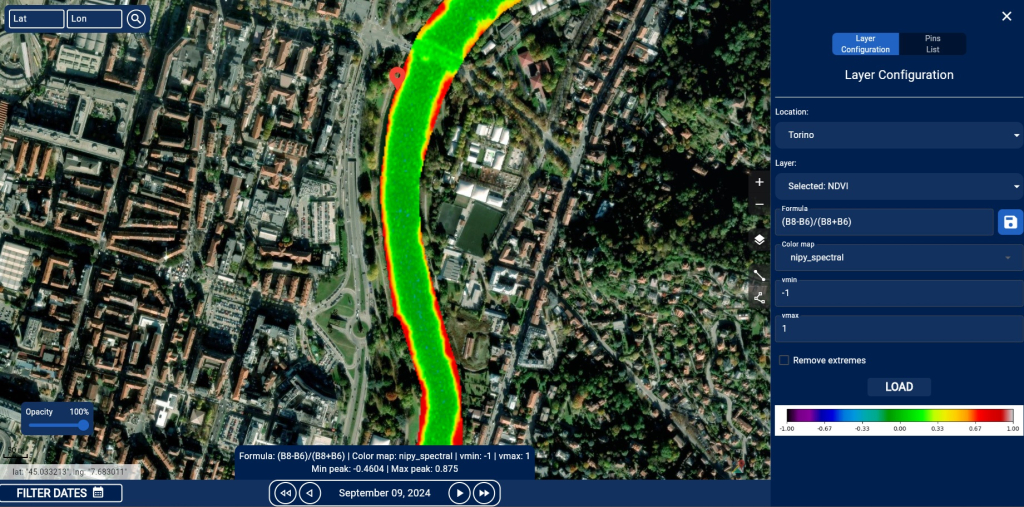
The interface also offers a side-by-side comparison feature for geospatial data, enabling the analysis of temporal variations, differences between two datasets, or comparisons of different indices on the same dates or at different points in time.
Each panel is individually configurable, with tools to customize formulas, color maps, and parameters. Ideal for monitoring environmental changes, such as vegetation evolution, it provides a seamless interactive experience and data overlay:
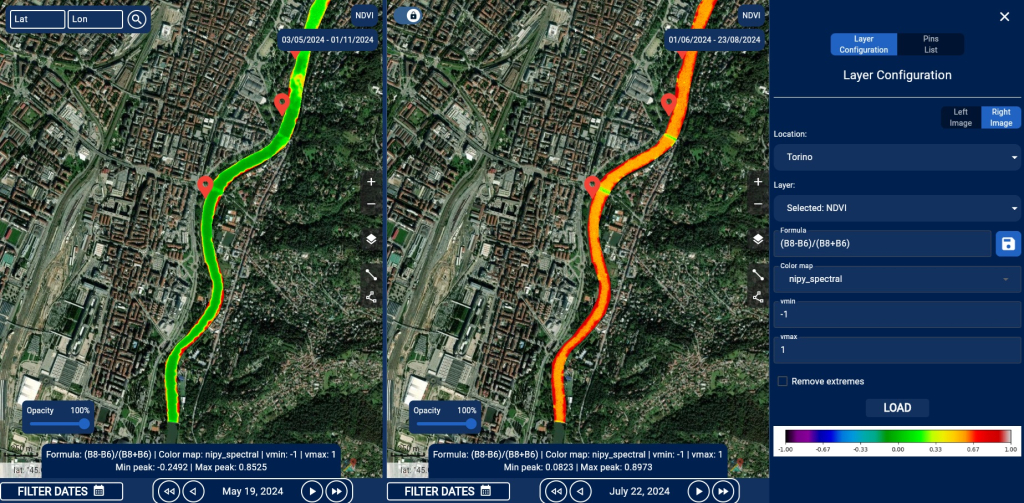
The interface integrates a “slideshow” system for advanced temporal analysis, allowing users to select specific dates or time intervals to dynamically observe and monitor variations in geospatial data, such as changes in vegetation or resource distribution.
This functionality is particularly useful for analyzing environmental trends and supporting decisions based on historical data and real-time updates:
NODES Ecosystem

Our partners



RiparianEye is part of the NODES project, receiving funds from MUR – Missione 4, Componente 2, Investimento 1.5 – Creazione e rafforzamento di “Ecosistemi dell’innovazione”, costruzione di “leader territoriali di R&S” – of PNRR with grant egreement no. ECS00000036
